Lactobacillus reuteri attenuated allergic
Jiangnan University, Yangzhou, China, 5 Department of Microbiology & Immunology, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore, 6 Wuxi Translational Medicine Research
Center and Jiangsu Translational Medicine Research Institute Wuxi Branch, Wuxi, China, 7 BeijingInnovation Centre of Food Nutrition and Human Health, Beijing Technology and Business University (BTBU), Beijing, China
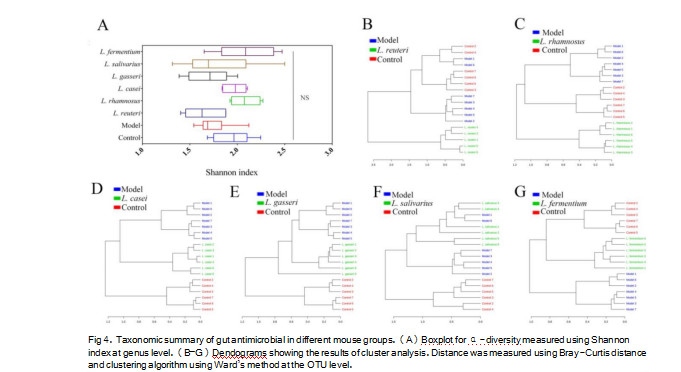
Using the results from hierarchical clustering, we categorized the Lactobacillus groups into three classes for further LEfSe analysis.
We found that 17 taxa sequences were significantlyaltered in the Lactobacillus groups. Rhodococcus, Streptococcus, Allobaculum, Blautia, Faecali-bacterium, Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Enterococcus increased whereas Turicibacter,
Anaerostipes, Coprococcus, and Adlercreutzia decreased in the Lactobacillus groups, compared with the model group. The abundance of Bacteroides, which decreased in the model group, increased only after L. rhamnosus administration. Prevotella, Eggerthella, Eubacterium, and Oscillospira were enriched in control (Fig 5A).