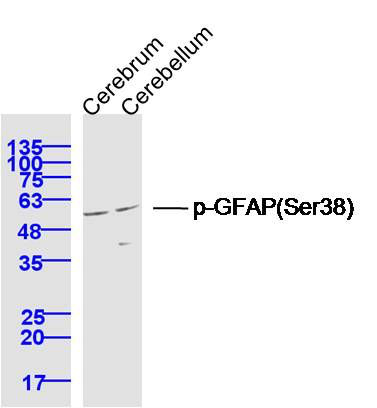
产品货号 : mlR13336
英文名称 : phospho-GFAP (Ser38)
中文名称 : 磷酸化胶质纤维酸性蛋白抗体
别 名 : GFAP (phospho S38); p-GFAP (Ser38); Astrocyte; FLJ45472; GFAP; Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein; Intermediate filament protein; GFAP_HUMAN.
产品类型 : 磷酸化抗体
研究领域 : 肿瘤 细胞生物 免疫学 神经生物学 信号转导 干细胞 细胞粘附分子 细胞骨架
抗体来源 : Rabbit
克隆类型 : Polyclonal
交叉反应 : Human, Mouse,
产品应用 : WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:500-1000 Flow-Cyt=1μg/Test
not yet tested in other applications.
optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
分 子 量 : 48kDa
细胞定位 : 细胞浆
性 状 : Lyophilized or Liquid
浓 度 : 1mg/ml
免 疫 原 : KLH conjugated synthesised phosphopeptide derived from human GFAP around the phosphorylation site of Ser38:RL(p-S)L
亚 型 : IgG
纯化方法 : affinity purified by Protein A
储 存 液 : 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
保存条件 : Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C.
PubMed : PubMed
产品介绍 : This gene encodes one of the major intermediate filament proteins of mature astrocytes. It is used as a marker to distinguish astrocytes from other glial cells during development. Mutations in this gene cause Alexander disease, a rare disorder of astrocytes in the central nervous system. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]
Function:
GFAP, a class-III intermediate filament, is a cell-specific marker that, during the development of the central nervous system, distinguishes astrocytes from other glial cells.
Subunit:
Interacts with SYNM. Isoform 3 interacts with PSEN1 (via N-terminus).
Subcellular Location:
Cytoplasm.
Tissue Specificity:
Expressed in cells lacking fibronectin.
Post-translational modifications:
Phosphorylated by PKN1.
DISEASE:
Defects in GFAP are a cause of Alexander disease (ALEXD) [MIM:203450]. Alexander disease is a rare disorder of the central nervous system. It is a progressive leukoencephalopathy whose hallmark is the widespread accumulation of Rosenthal fibers which are cytoplasmic inclusions in astrocytes. The most common form affects infants and young children, and is characterized by progressive failure of central myelination, usually leading to death usually within the first decade. Infants with Alexander disease develop a leukoencephalopathy with macrocephaly, seizures, and psychomotor retardation. Patients with juvenile or adult forms typically experience ataxia, bulbar signs and spasticity, and a more slowly progressive course.
Similarity:
Belongs to the intermediate filament family.
SWISS:
P14136
Gene ID:
2670
Important Note:
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
产品图片