产品货号 : mlR21450
英文名称 : TTR/Prealbumin
中文名称 : 转甲状腺素蛋白/前白蛋白抗体
别 名 : Transthyretin; Amyloid polyneuropathy; Amyloidosis I; ATTR; Dysprealbuminemic euthyroidal hyperthyroxinemia; Dystransthyretinemic hyperthyroxinemia; HsT2651; PALB; Prealbumin amyloidosis type I; Senile systemic amyloidosis; TBPA; Transthyretin; TTR; TTR protein; prealbumin; TTHY_HUMAN.
研究领域 : 肿瘤 结合蛋白 细胞类型标志物
抗体来源 : Rabbit
克隆类型 : Polyclonal
交叉反应 : Human,
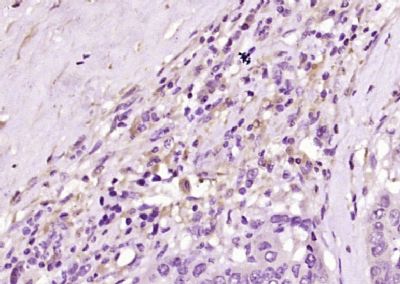
产品应用 : WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:500-1000 IHC-P=1:400-800 IHC-F=1:400-800 ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 (石蜡切片需做抗原修复)
not yet tested in other applications.
optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
细胞定位 : 细胞核
性 状 : Lyophilized or Liquid
浓 度 : 1mg/ml
免 疫 原 : KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human TTR/Prealbumin :51-147/147
亚 型 : IgG
纯化方法 : affinity purified by Protein A
储 存 液 : 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol.
保存条件 : Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. The lyophilized antibody is stable at room temperature for at least one month and for greater than a year when kept at -20°C. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C.
PubMed : PubMed
产品介绍 : This gene encodes transthyretin, one of the three prealbumins including alpha-1-antitrypsin, transthyretin and orosomucoid. Transthyretin is a carrier protein; it transports thyroid hormones in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid, and also transports retinol (vitamin A) in the plasma. The protein consists of a tetramer of identical subunits. More than 80 different mutations in this gene have been reported; most mutations are related to amyloid deposition, affecting predominantly peripheral nerve and/or the heart, and a small portion of the gene mutations is non-amyloidogenic. The diseases caused by mutations include amyloidotic polyneuropathy, euthyroid hyperthyroxinaemia, amyloidotic vitreous opacities, cardiomyopathy, oculoleptomeningeal amyloidosis, meningocerebrovascular amyloidosis, carpal tunnel syndrome, etc. [provided by RefSeq]
Function:
Thyroid hormone-binding protein. Probably transports thyroxine from the bloodstream to the brain.
Subunit:
Homotetramer. Dimer of dimers. In the homotetramer, subunits assemble around a central channel that can accommodate two ligand molecules. Interacts with RBP4.
Subcellular Location:
Secreted. Cytoplasm.
Tissue Specificity:
Detected in serum and cerebrospinal fluid (at protein level). Highly expressed in choroid plexus epithelial cells. Detected in retina pigment epithelium and liver.
Post-translational modifications:
Not glycosylated under normal conditions. Following unfolding, caused for example by variant AMYL-TTR 'Gly-38', the cryptic Asn-118 site is exposed and glycosylated by STT3B-containing OST complex, leading to its degradation by the ER-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway.
DISEASE:
Defects in TTR are the cause of amyloidosis transthyretin-related (AMYL-TTR) [MIM:105210]. A hereditary eneralized amyloidosis due to transthyretin amyloid deposition. Protein fibrils can form in different tissues leading to amyloid polyneuropathies, amyloidotic cardiomyopathy, carpal tunnel syndrome, systemic senile amyloidosis. The disease includes leptomeningeal amyloidosis that is characterized by primary involvement of the central nervous system. Neuropathologic examination shows amyloid in the walls of leptomeningeal vessels, in pia arachnoid, and subpial deposits. Some patients also develop vitreous amyloid deposition that leads to visual impairment (oculoleptomeningeal amyloidosis). Clinical features include seizures, stroke-like episodes, dementia, psychomotor deterioration, variable amyloid deposition in the vitreous humor.
Defects in TTR are a cause of hyperthyroxinemia dystransthyretinemic euthyroidal (HTDE) [MIM:145680]. It is a condition characterized by elevation of total and free thyroxine in healthy, euthyroid persons without detectable binding protein abnormalities.
Defects in TTR are a cause of carpal tunnel syndrome type 1 (CTS1) [MIM:115430]. It is a condition characterized by entrapment of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel. Symptoms include burning pain and paresthesias involving the ventral surface of the hand and fingers which may radiate proximally. Impairment of sensation in the distribution of the median nerve and thenar muscle atrophy may occur. This condition may be associated with repetitive occupational trauma, wrist injuries, amyloid neuropathies, rheumatoid arthritis.
Similarity:
Belongs to the transthyretin family
SWISS:
P02766
Gene ID:
7276
Important Note:
This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications.
产品图片